Global Warming Climate Dangers
Global warming has NOTstopped
First, 2014 was a record for global warming. Dangerous Arctic summer sea ice melting and dangerous global extreme weather events are still increasing. Global heating is accelerating because more heat is going into the deeper ocean warming (and melting more planetary ice).
The many great dangers of global warming and climate change, that impact on human population and survival, have been recognized for a great many years.
Billions of the most vulnerable
We are well aware than billions of most vulnerable people living in the most climate change change regions face increasing dangerous impacts from additional losses of water food and health. Billions face catastrophic population health and survival impacts in the near term . What we are unaware of is that because of already committed (locked in) global warming, the well off Global North is now vulnerable.
Extreme weather events
Extreme weather is treated as one category of climate change impacts. As such it is the most dangerous to human health and to crops. IN the most climate vulnerable regions where agriculture is labour intensive these are mutually increasing.
Extreme weather is increasing, and recent research has linked the increase to global warming and climate change.
Matter of survival
Measures to reverse increasing global emissions have been delayed for so long (20 years since the UN climate convention), that global climate change now is a 'threat to the very survival of humanity' (UNEO GEO 4 2007).
Runaway
The greatest dangers involve the Arctic, which due to Arctic amplification of global warming is now warming three times the global average (double averaged over 100 years).
The worst of all dangers is so-called runaway global climate change or rapid irreversibly increasing global heating. This results from the 'vicious cycles' of global warming-Arctic amplification and Arctic huge sources of greenhouse gas feedback emissions.

Arctic dangers
All the Arctic amplifying feedbacks that make up the runaway danger situation are operant.
Arctic: loss of albedo cooling- more warming
There is a rapid declining trend of Arctic/Far North snow cover, Arctic summer sea ice extent, and Greenland ice sheet surface albedo (from melting of ice sheet surface).
Declining Arctic albedo first amplifies Arctic warming, then the northern hemisphere, and then even global warming.
Arctic: increase Arctic feedback GHG emissions
The big feedback danger has been Arctic methane, because most Arctic cold/frozen stores of carbon release mostly methane when warmed. Right now subarctic wetland peat is emitting increasing amounts of methane, thawing permafrost is emitting mainly methane-but also CO2 and nitrous oxide, and subsea floor methane gas is venting to the atmosphere from the shallow huge East Siberian continental shelf.
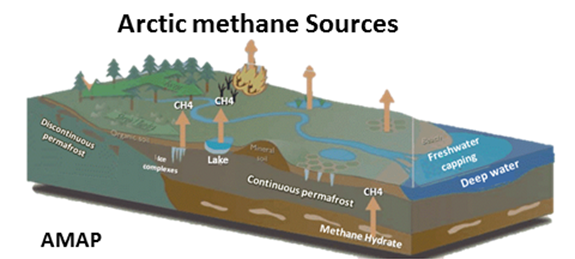
Methane has 86 X the global warming effect of CO2 over 20 year period and nitrous oxide has 290 X CO2's warming capacity, making the Arctic feedbacks though small today a catastrophic planetary danger. Arctic feedbacks are not included in the IPCC assessments (UNEP 2012 Policy Implications of Warming Permafrost).
Food security
It is intuitive that warming the surface of the planet and changing the planet's climate would be highly dangerous to agriculture, and the fact is it is.
Food: multiple adverse impacts
There are very many adverse impacts to agriculture of global warming and climate change, that far outweigh the few potential benefits.
- Climate variability (unreliable seasons and unseasonal weather)
- Extreme heat
- Increased ground level ozone - (increases with warming is toxic to green plants)
- Drought
- Drying of soil
- Severe storms
- Torrential rains
- Floods
- Soil erosion
- Increased and resistant insect pests
- Increased and resistant weeds
- Increased plant pathogens
However assessments, relying on climate crop computer models, still in the development stage, have projected that the well off temperate northern hemisphere would actually benefit by increased crop yields and only Africa and the lower latitudes would lose food production.
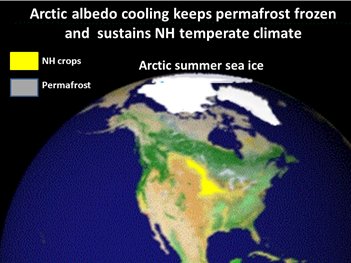
Some recent papers on extremes have shown that the crop production of the Global North is highly vulnerable, and another rapidly increasing factor is the loss of Arctic albedo cooling.
NH Food: Arctic albedo
Scientists call the Arctic summer sea ice the air conditioner of the entire northern hemisphere and predict the the loss of millions of square miles of sea ice will change the climate of the now temperate northern hemisphere. The NH is already being affected by increased climate variability (unseasonal weather) and increased extreme weather events, like heat waves droughts and floods. Because committed (locked in) global warming is much higher than today's 0.8C the world's best food producing regions of the NH are in trouble.
The 2016 Planetary Health Alliance (2019 VIDEO)
Video Dr. H. Montgomery's 2018 lecture says it all
Lancet Countdown (Nov)2018 Report for policy makers
2017 WHO 5th Climate & Health Summit
2014 Lancet From Public to Planetary Health:
A Manifesto
2014 BMJ Climate Change & Human Survival
2014 BMJ Climate Change
is a Health Emergency
IPCC 5th Assessment
Climate & Health Council